

- Socks5 proxy list software#
- Socks5 proxy list code#
- Socks5 proxy list free#
SOCKS4a extends the SOCKS4 protocol to allow a client to specify a destination domain name rather than an IP address this is useful when the client itself cannot resolve the destination host's domain name to an IP address. The command field may be 0x01 for "connect" or 0x02 for "bind" the "bind" command allows incoming connections for protocols such as active FTP. The SOCKS4 protocol specifies that the values of these bytes should be ignored.įrom this point onwards, any data sent from the SOCKS client to the SOCKS server is relayed to 66.102.7.99, and vice versa. Server: 0x00 | 0x5A | 0xXX 0xXX | 0xXX 0xXX 0xXX 0xXX.The last field is "Fred" in ASCII, followed by a null byte.

Request failed because client's identd could not confirm the user ID in the requestĭSTPORT destination port, meaningful if granted in BIND, otherwise ignore DSTIP destination IP, as above – the ip:port the client should bind toįor example, this a SOCKS4 request to connect Fred to 66.102.7.99:80, the server replies with an "OK": Request failed because client is not running identd (or not reachable from server)
Socks5 proxy list code#
VN reply version, null byte REP reply code Byte
0x01 = establish a TCP/IP stream connectionĭSTPORT 2-byte port number (in network byte order) DESTIP IPv4 Address, 4 bytes (in network byte order) ID the user ID string, variable length, null-terminated. VER SOCKS version number, 0x04 for this version CMD command code: Socks5 proxy list free#
This can free the user from the limitations of connecting only to a predefined remote port and server.Ī typical SOCKS4 connection request looks like this:
Some SSH suites, such as OpenSSH, support dynamic port forwarding that allows the user to create a local SOCKS proxy. Providing similar functionality to a virtual private network, allowing connections to be forwarded to a server's "local" network:. Socks5 proxy list software#
The Tor onion proxy software presents a SOCKS interface to its clients. Since SOCKS is very detectable, a common approach is to present a SOCKS interface for more sophisticated protocols: A circumvention tool, allowing traffic to bypass Internet filtering to access content otherwise blocked, e.g., by governments, workplaces, schools, and country-specific web services. The circuit/session level nature of SOCKS make it a versatile tool in forwarding any TCP (or UDP since SOCKS5) traffic, creating an interface for all types of routing tools. SOCKS is a de facto standard for circuit-level gateways (level 5 gateways). The protocol was developed in collaboration with Aventail Corporation, which markets the technology outside of Asia. It was approved by the IETF in 1996 as RFC 1928 (authored by: M. The SOCKS5 protocol was originally a security protocol that made firewalls and other security products easier to administer. ( Blue Coat Systems bought out Permeo Technologies, and were in turn acquired by Symantec.) The SOCKS reference architecture and client are owned by Permeo Technologies, a spin-off from NEC. The protocol was extended to version 4 by Ying-Da Lee of NEC. After MIPS was taken over by Silicon Graphics in 1992, Koblas presented a paper on SOCKS at that year's Usenix Security Symposium, making SOCKS publicly available. The protocol was originally developed/designed by David Koblas, a system administrator of MIPS Computer Systems. 4.1.2 Other programs providing SOCKS server interface. 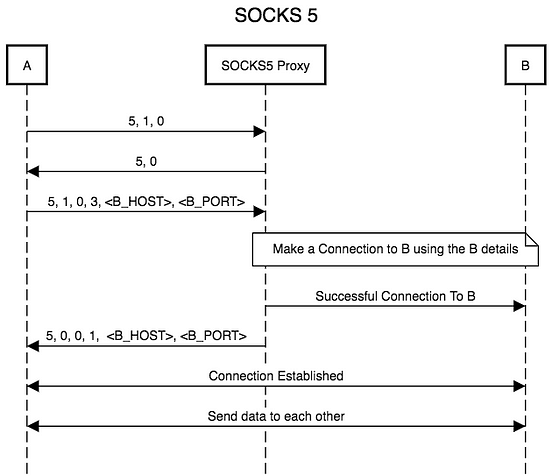
4.1.1 SOCKS proxy server implementations.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
